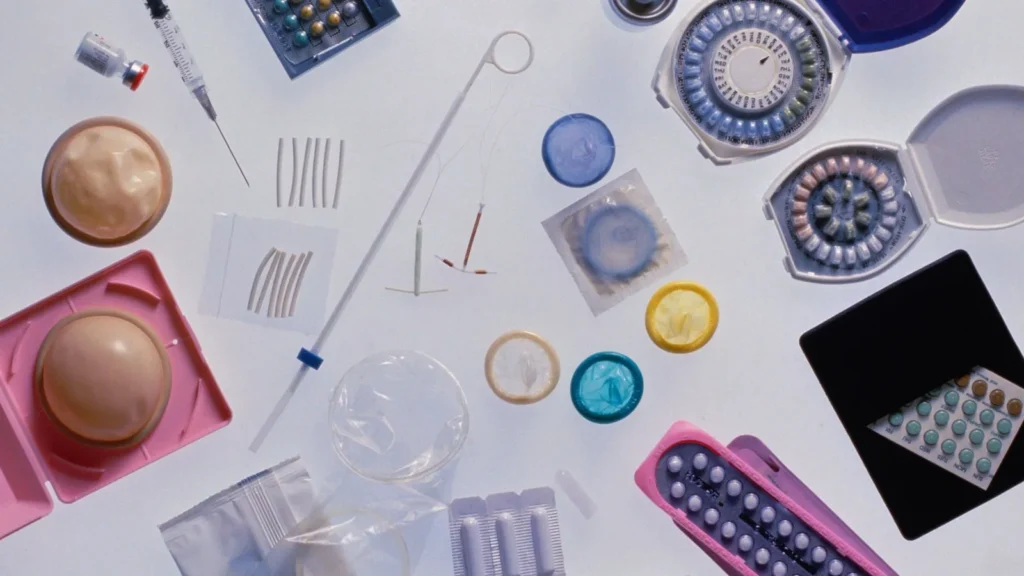
Navigating the world of birth control can be overwhelming with numerous options available today. From hormonal methods like pills and patches to non-hormonal alternatives such as copper IUDs, each type of birth control offers different benefits, effectiveness rates, and potential side effects.
The best birth control option varies for each woman depending on her health history, lifestyle, and reproductive goals. Some may prefer the convenience of long-acting reversible contraceptives like IUDs or implants with over 99% effectiveness, while others might choose daily pills or barrier methods that can be used as needed.
Making an informed decision involves understanding how each method works and discussing personal factors with a healthcare provider. Women should consider effectiveness, convenience, hormone sensitivity, and future pregnancy plans when selecting a birth control method that aligns with their needs.
Understanding Birth Control Options
Birth control methods vary widely in their effectiveness, side effects, and convenience. Each option offers unique benefits and considerations that should be weighed carefully based on individual health needs and lifestyle factors.
Hormonal Methods
Hormonal contraceptives work by preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, or thinning the uterine lining. Combined hormonal contraceptives contain both estrogen and progestin, while progestin-only methods exclude estrogen, providing different types of birth control options.
The pill requires daily adherence and is approximately 91% effective with typical use, making it a common method of birth control for many women. Users must take it at the same time each day for maximum effectiveness.
Hormonal patches are changed weekly and deliver hormones through the skin. The vaginal ring is inserted monthly and releases hormones directly into the reproductive system, providing a convenient method of birth control.
Injectable contraceptives like Depo-Provera provide protection for three months with each shot, allowing women to use birth control without a prescription. These methods offer convenience for those who struggle with daily pill routines.
Hormonal implants, such as Nexplanon, are placed under the skin of the upper arm and can prevent pregnancy for up to five years. They have over 99% effectiveness, making them one of the most reliable options available.
Barrier Methods
Barrier methods physically prevent sperm from reaching an egg. Male condoms, made from latex, polyurethane, or lambskin, are 85% effective with typical use and also provide STI protection, making them a versatile method of birth control.
Female condoms are inserted into the vagina before intercourse and offer similar STI protection. They give women more control over their protection.
Diaphragms and cervical caps must be fitted by healthcare providers and used with spermicide. These reusable devices are inserted before sex and must remain in place for several hours afterward.
The sponge contains spermicide and can be inserted up to 24 hours before intercourse. It’s more effective for women who haven’t given birth.
Spermicides can be used alone but are more effective when combined with other barrier methods. They come in various forms including creams, gels, and suppositories.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus by healthcare providers. They provide long-term, reversible contraception with effectiveness rates over 99%.
Hormonal IUDs release levonorgestrel, which thickens cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining. These can last between 3-8 years depending on the brand and may reduce menstrual bleeding and cramping.
Copper IUDs (ParaGard) work by creating an environment toxic to sperm and can remain effective for up to 10 years. They offer hormone-free protection but may increase menstrual bleeding.
IUD insertion takes only a few minutes but may cause cramping. Most women can return to normal activities immediately after placement.
Both types can be removed at any time by a healthcare professional with a quick return to fertility.
Natural and Fertility Awareness Methods
Fertility awareness methods involve tracking fertility signals to identify fertile days. These methods require consistent monitoring and abstinence during fertile periods.
The calendar method tracks menstrual cycles to predict ovulation. The temperature method monitors basal body temperature, which rises after ovulation.
The cervical mucus method observes changes in vaginal discharge throughout the cycle. More effective approaches combine these techniques into the symptothermal method.
These methods cost nothing and have no physical side effects. However, they require significant commitment and education to use correctly.
Typical effectiveness rates range from 76-88% with standard use. Couples seeking higher effectiveness should consider additional protection during fertile days.
Selecting the Right Birth Control
Choosing the right birth control method requires careful consideration of effectiveness rates, personal lifestyle factors, and potential health implications. The ideal method balances reliability with individual needs and medical history.
Considerations for Effectiveness
Effectiveness should be a primary factor when selecting birth control. Methods like IUDs and implants offer over 99% effectiveness with minimal user error, making them excellent choices for those seeking maximum pregnancy prevention.
Hormonal methods such as pills, patches, and rings are 91-94% effective with typical use but can reach 99% with perfect use. User compliance significantly impacts their reliability.
Barrier methods like condoms have lower typical effectiveness rates (82-85%) but offer the added benefit of protecting against sexually transmitted infections. Many women combine methods for enhanced protection.
Emergency contraception serves as a backup option when primary methods fail but shouldn’t replace regular birth control.
Understanding failure rates helps set realistic expectations. Healthcare providers can provide personalized effectiveness data based on age, health status, and lifestyle factors.
Lifestyle and Personal Preferences
Daily schedules and routines significantly impact birth control success. Women with busy or unpredictable schedules may struggle with methods requiring daily attention like pills.
Long-acting options like IUDs or implants can be ideal for those who prefer “set and forget” contraception. These methods eliminate daily maintenance concerns.
Sexual frequency and relationship status matter too. Sexually active individuals in monogamous relationships might prefer different methods than those with multiple partners.
Cost and accessibility considerations include:
- Insurance coverage
- Need for prescriptions
- Frequency of doctor visits
- Long-term versus short-term costs
Some women prioritize methods that don’t interfere with spontaneity during intimacy, preferring options that can be used every time you have sex. Others may choose methods based on their plans for future pregnancy and how quickly fertility returns after discontinuation, particularly if they want to get pregnant soon.
Health Risks and Side Effects
Every birth control method carries potential side effects that vary by individual. Hormonal options may cause mood changes, Weight gain can be a potential side effect associated with some methods of birth control., or nausea This can occur in some women but not others, highlighting the variability in responses to different types of birth control.
Pre-existing health conditions significantly impact contraceptive choices. Women with high blood pressure, history of blood clots, or certain cancers should avoid some hormonal methods.
Age is another important factor. Women over 35 who smoke face increased risks with estrogen-containing contraceptives.
Common side effects to consider include:
- Menstrual changes (lighter, heavier, or absent periods)
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Mood fluctuations
Serious complications are rare but possible. These include blood clots, stroke, and heart attack, particularly with combined hormonal methods.
Regular follow-up appointments help monitor for side effects and ensure the chosen method of birth control is effective. A healthcare provider can recommend alternative options if side effects become problematic.
Non-Traditional and Permanent Methods
Beyond daily pills and barrier methods, several birth control options offer either emergency solutions or long-term to permanent protection against pregnancy.
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception provides a backup method when other birth control fails or wasn’t used. The most common option is the “morning-after pill,” available in two forms: levonorgestrel (Plan B One-Step) and ulipristal acetate (ella). Levonorgestrel works best when taken within 72 hours after unprotected sex, while ulipristal remains effective for up to 5 days.
Copper IUDs also function as emergency contraception when inserted within 5 days of unprotected intercourse. They offer the added benefit of continuing to prevent pregnancy for up to 10 years.
Emergency contraception works primarily by delaying or preventing ovulation. It does not terminate an existing pregnancy and becomes less effective with higher body weight.
Many healthcare providers, including specialized clinics, offer emergency contraception services and counseling about future birth control options, ensuring women have access to different types of birth control.
Sterilization Procedures
Sterilization provides permanent birth control for those who are certain they don’t want children. These procedures are generally not reversible and should be considered final decisions.
For women, tubal ligation (often called “getting your tubes tied”) involves cutting, tying, or blocking the fallopian tubes. This prevents eggs from reaching the uterus and sperm from reaching the egg. The procedure can be performed laparoscopically with small incisions and minimal recovery time.
Although not a female method, vasectomy is worth mentioning as a permanent option for male partners. This simple outpatient procedure cuts or blocks the tubes that carry sperm, which is a permanent method of birth control. It’s less invasive than tubal ligation with a shorter recovery period, making it a preferred method of birth control for many women.
Both procedures are highly effective with failure rates below 1%. Insurance typically covers these procedures, but requirements vary by provider and location.
Frequently Asked Questions
Choosing the right birth control method involves weighing several factors including effectiveness, side effects, convenience, and personal health history. The answers below address common concerns to help women make informed decisions about their contraceptive options and the associated risks of blood clots.
How can I select a birth control method that minimizes side effects?
Consider your medical history, discuss options with a healthcare provider at a reputable clinic like LocalMD, and possibly trial methods with fewer hormones such as IUDs, barrier methods, or low-dose pills to identify what works best for your body chemistry.
What are the most reliable forms of birth control available today?
Hormonal IUDs, implants, and sterilization offer the highest effectiveness rates (over 99%), followed by hormonal methods like pills, patches, and rings (91-94% with typical use), while barrier methods provide moderate protection.
What birth control options have the least impact on weight?
Non-hormonal methods like copper IUDs, barrier methods, and fertility awareness typically have no impact on weight, while progestin-only options generally cause fewer weight-related side effects than combined hormonal contraceptives.
How does the birth control implant compare to other methods in terms of safety and effectiveness?
The implant offers over 99% effectiveness, requires minimal maintenance for up to 5 years, has a quick reversibility profile, and presents fewer serious risks than methods containing estrogen, making it both highly safe and effective for most women.
What are the primary considerations when choosing a birth control pill?
Consider your health history (particularly regarding migraines, blood clots, or smoking), potential side effects, pill-taking consistency, whether you need help with menstrual symptoms, and if you plan to become pregnant soon.
Can you compare the efficacy and convenience of the birth control patch and the shot?
The patch requires weekly application with 91-94% typical use effectiveness, while the shot offers 94% effectiveness with quarterly injections, making the shot more convenient but less user-controlled than the patch, which remains visible and easily discontinued.