Tubal ligation is a permanent form of birth control that many women choose, but circumstances can change, leading some to consider whether reversing the procedure is an option. The success of a tubal ligation reversal largely depends on various factors, including the method used for the initial procedure and the woman’s age and health.
Those contemplating this reversal should understand that while success rates can vary, they typically range between 40% to 80% for women who undergo the procedure within a certain timeframe. Many women find hope in the potential to conceive again through this method, but it is essential to consult with a qualified specialist who can provide a tailored approach based on individual health and history.
LocalMD offers resources for those seeking information on tubal reversal procedures and can connect individuals with knowledgeable healthcare professionals. Understanding the ins and outs of tubal ligation reversal can empower women to make informed decisions regarding their reproductive health.
Understanding Tubal Ligation and Reversal
This section explains what tubal ligation is and the procedure involved in its reversal. Tubal ligation is often chosen for permanent birth control, while reversal surgery aims to reconnect the fallopian tubes.
What Is Tubal Ligation?
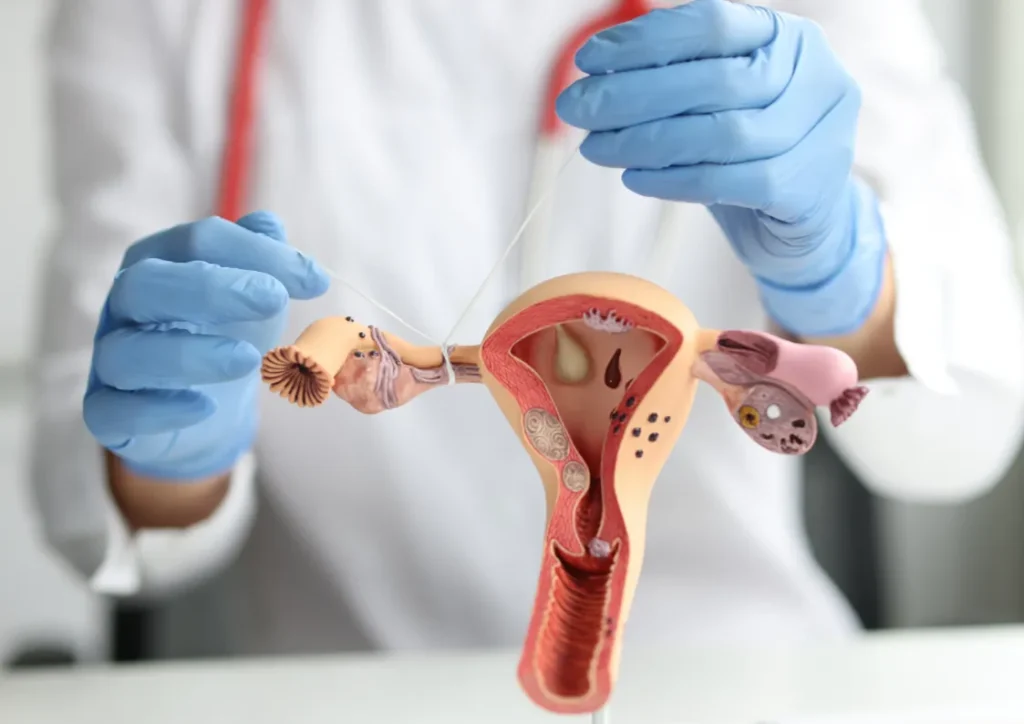
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure designed to prevent pregnancy by permanently blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes. During this procedure, a surgeon may cut, tie, or cauterize the tubes to stop the passage of eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes to an hour. Recovery times vary, but most individuals can return to normal activities within a few days. Tubal ligation is considered an effective method for permanent birth control, with a failure rate of less than 1%.
It’s essential to discuss all options thoroughly with a healthcare provider before deciding on this permanent solution.
What Is Tubal Ligation Reversal?
Tubal ligation reversal is a surgical procedure aimed at reconnecting the fallopian tubes after they have been ligated. This surgery may be performed using different techniques, including laparoscopic or open surgery, depending on the individual’s circumstances and health.
The success of reversal surgery often depends on the type of tubal ligation performed and the individual’s age and fertility status. While many people can conceive after reversal, fertility rates can vary.
Cost and recovery can be significant factors as well. This procedure does not guarantee pregnancy, and individuals should consult specialists to discuss their options and expectations.
The Tubal Reversal Procedure
The tubal reversal procedure is a surgical technique aimed at reconnecting the fallopian tubes after a tubal ligation. Understanding the process, types of surgeries available, and post-operative care is crucial for those considering this option.
Pre-Surgery Considerations
Before undergoing a tubal reversal, it is essential to assess individual health factors. A thorough evaluation, including medical history and pelvic examinations, helps determine candidacy.
Patients should consider the type of previous tubal ligation, as some methods may be more difficult to reverse than others.
Additionally, tests like hysterosalpingography (HSG) can visualize the fallopian tubes to confirm their condition.
Discussing anesthesia options is also vital. Most reversals use general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is comfortable throughout the procedure.
Types of Tubal Ligation Reversal Surgeries
There are primarily two types of tubal ligation reversal surgeries: laparoscopic and open surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive. It involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgeon. This method typically results in quicker recovery times and less scarring.
Open surgery, or mini-laparotomy, involves a larger incision and is considered when more extensive repair is needed.
Surgeons will choose the appropriate technique based on the tubal ligation type and patient specifics.
The success of the surgery largely depends on the remaining length of the fallopian tubes after ligation.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from a tubal reversal varies depending on the surgical technique used.
After laparoscopic surgery, most patients can go home the same day. They may experience mild discomfort, which is manageable with prescribed pain relief.
Open surgery may require a longer hospital stay and more extensive recovery time.
Post-operative care includes monitoring for signs of infection, avoiding strenuous activities, and following up with the surgeon.
Patients should discuss their recovery plan with their healthcare provider to ensure a successful healing process.
Success Rates and Potential Outcomes
The success of tubal ligation reversal varies based on multiple factors. Understanding these success rates and potential outcomes can help individuals considering this procedure.
Evaluating Success Rates
Success rates for tubal ligation reversals generally range between 40% to 80%. Data from reputable sources, including the Mayo Clinic, indicate that the likelihood of becoming pregnant largely depends on the method of the original tubal ligation.
For instance, the reversal procedure is often more successful in cases where the fallopian tubes were clipped rather than cut. The location of the ligation also plays a crucial role in determining the success of the process.
Factors Influencing Success
Several factors influence the chance of getting pregnant after a tubal ligation reversal. Key considerations include:
- Age: Women under 35 tend to have higher success rates.
- Type of Ligation: As mentioned, different surgical methods yield varying results.
- Overall Health: The woman’s reproductive health and partner’s sperm quality are vital.
Best candidates for reversal are those who have had their tubes tied for a shorter period and have no underlying fertility issues.
Risks and Complications
The risk of ectopic pregnancy after a tubal reversal is notable and can affect about 10% of cases. This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
Other potential complications may include infection or hemorrhaging. It’s essential for patients to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider before proceeding. The decision should consider the individual’s health history and reason for the reversal, ensuring they’re well-informed about the process.
Alternatives and Considerations
When considering alternatives to tubal ligation reversal, options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) become prominent. Evaluating these options requires careful thought about personal circumstances, including health factors and future family planning goals.
Alternatives to Tubal Ligation Reversal
One primary alternative is in vitro fertilization (IVF). This procedure involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then implanting it in the uterus. IVF can be a viable option for women who wish to conceive after a tubal ligation, especially when the reversal is not feasible due to medical reasons.
Other alternatives include adoption and surrogacy. These options offer family-building paths without the need for surgical intervention. Additionally, methods like electrocautery may be used in some cases to treat specific reproductive health issues, though they do not directly relate to reversing a tubal ligation.
Deciding on Tubal Reversal vs Alternatives
The decision to pursue tubal reversal or alternative routes should consider several factors. Age, health status, and fertility potential play critical roles in this choice. For instance, younger women may have a higher chance of success with either a tubal reversal or IVF.
Cost is another significant factor. Tubal reversal surgeries can be expensive, and IVF clinics often have varying price structures. Couples should also evaluate their emotional readiness for potential challenges, including unsuccessful attempts. Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide insights tailored to individual circumstances and help in making an informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding tubal ligation reversal. Key topics include cost, age considerations, timing for conception attempts, chances of success, affordable options, and the possibility of natural conception thereafter.
What is the average cost of a tubal ligation reversal?
The average cost of a tubal ligation reversal typically ranges from $5,000 to $15,000.
At what age is tubal ligation reversal still considered feasible?
Tubal ligation reversal is generally feasible for women under the age of 40.
How long should one wait after a tubal ligation reversal before attempting to conceive?
It is advisable to wait at least three to six months after the procedure before trying to conceive.
What are the chances of conceiving after a tubal ligation reversal?
Success rates for conception after a tubal ligation reversal range from 40% to 80%, depending on various factors.
Are there affordable options for tubal reversal procedures available?
Some clinics and financing programs offer options to make tubal reversal procedures more affordable.
Is natural conception possible after having tubal ligation with cutting and burning?
Natural conception is less likely after cutting and burning methods, but it is still possible depending on individual circumstances.